
Neutering
If you have no plans of breeding your female cat, we recommend having her neutered. These days contraceptive pills are only ever used in exceptional cases (to temporarily postpone a breeding cat going into season) due to the many side effects they may have. The spaying of a female cat is a relatively small and quick procedure.
We recommend that cats, both male and female, are neutered after the age of six months.
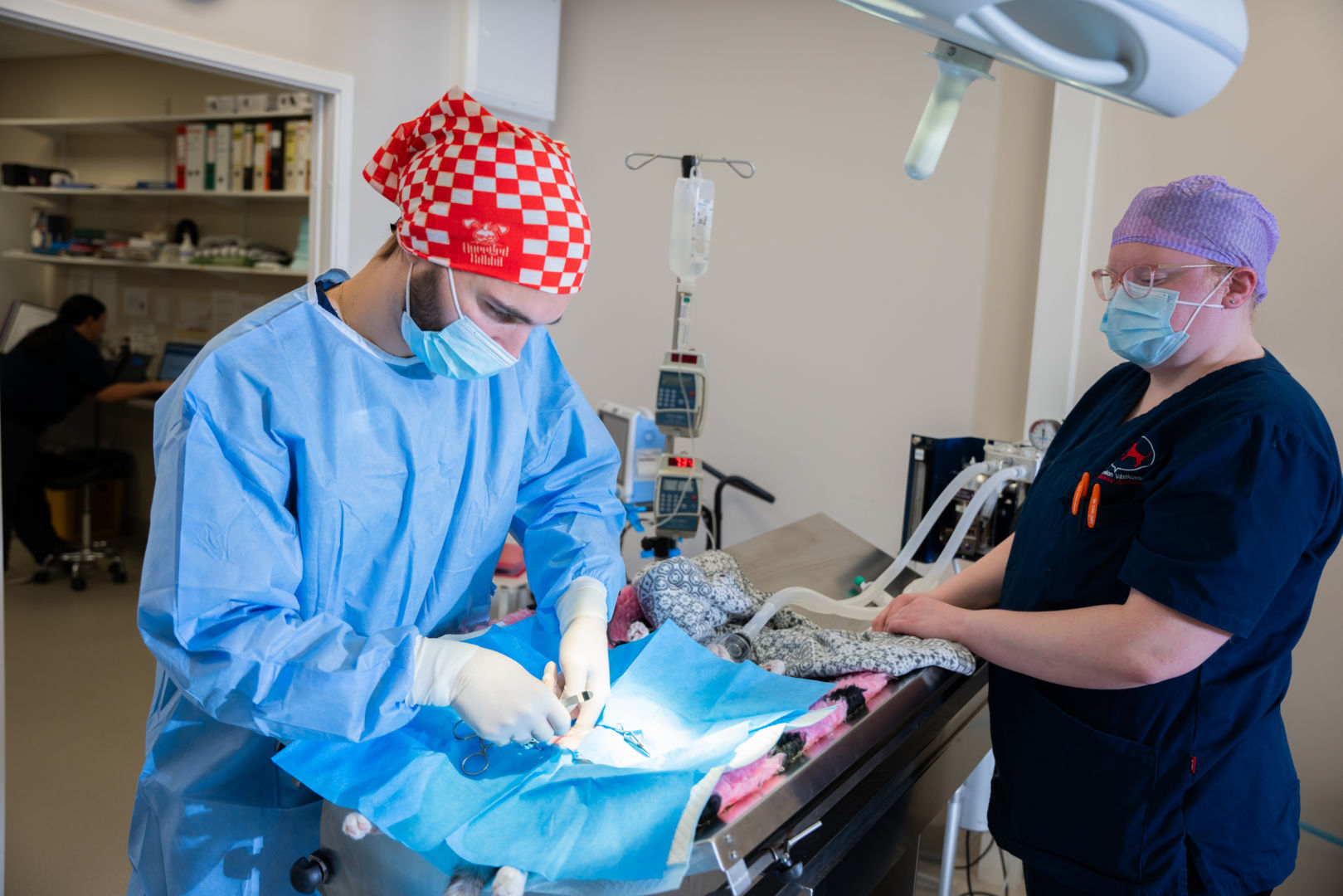
When a cat comes to the clinic for neutering, we will first carry out a general examination. We weigh the cat carefully, estimate its general condition and listen to its heart. Cats are anaesthetised with an intramuscular injection. The cat´s oxygen intake is supported by an oxygen mask through the whole procedure.
We shave the fur from the area of the incision and keep the cat on a soft surface in a warm place to prevent its body temperature from dropping too much (as tends to happen with animals under anaesthesia).
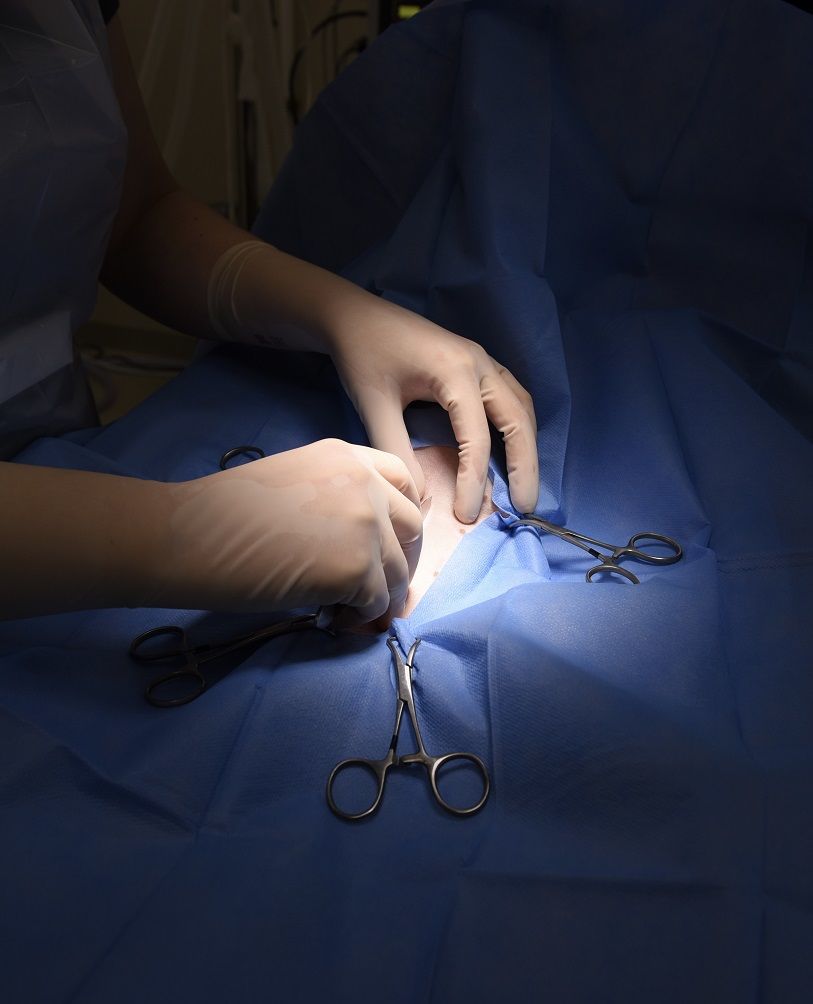
Female cats will also have a cannula inserted and will be sedated through an intravenous drip throughout the operation and when waking up (this accelerates waking up and ensures renal tissue perfusion). The removal of the ovaries requires a small incision in the area of the navel. After the procedure, muscles and the skin are sewn with stitches that will dissolve, which means there is no need to bring the cat to the clinic for stitch removal. The incision is about 2 cm long. Both male and female cats are given effective pain medication, meloxicam, buprenorfin (opioid) and anti-emetic and the price of the operation also includes a tasteless painkiller that is administered orally for the next couple of days. We dress the cat in a string recovery suit and put a surgical plaster on top of the wound. A cone is hardly ever necessary.
Complications are extremely rare in these operations. Sometimes the incision can become infected if the cat wants to continuously lick it with its rough tongue.
When bringing a cat in for neutering, we recommend you have a travel crate with plenty of insulating padding at the bottom.
The neutering of a female cat will take about 45 minutes, but we will keep her at the clinic for observation for a few hours and when she has woken up you can take your cat home.
All our veterinarians perform neutering operations for cats.
In many countries, female cats are neutered when they are still kittens, and this has not been found to have any adverse effects on their physical development. In the Nordic countries, cats are most often neutered when they are a little older. The minimum weight is 1 kg.

If you have not planned to breed your female dog, or she is past the breeding age, it makes sense to have her spayed. Studies show that neutering performed at an early age (before the dog’s second or third heat) is a highly effective way to prevent the risk of mammary cancer. Of course, a hysterectomy at any age will prevent the inflammation of the uterus (metritis) and your dog will stop going into heat and having phantom pregnancies.
The spaying of a female dog involves making an incision in the abdominal cavity and either removing her ovaries (ovariectomy; for young dogs with no abnormalities of the womb) or, if necessary, the entire uterus and ovaries (ovariohysterectomy). Your dog will be given pain medication for a few days. She is given a cone and/or a recovery suit to prevent the licking of the wound. The dog should not have any strenuous exercise for a while to ensure that the wound heals as quickly as possible.
We also have possibility for endoscopic surgery for your 10-65 kg bitch – with minimum period of time needed for healing.

If you have several rabbits, we recommend neutering female ones. This will prevent unnecessary fights.
Castration

Almost all male cats are castrated. Only cats intended for breeding are left uncastrated for the duration of breeding. A male cat usually reaches sexual maturity at around 6–8 months, an age when his urine starts to smell stronger and he may start to mark his territory with urine, be restless and beg to go out.
We anaesthetise the cat with an intramuscular injection, numb his testicles with a local anaesthetic and remove them through two incisions that will not have any stitches you can see from the outside. The cat will be given meloxicam for pain relief, an anti-inflammatory drug known as buprenorphine and an opioid.
There is no need for a cone to prevent licking.

Male dogs are castrated more and more often today. A male dog reaches sexual maturity usually around the age of 6–12 months. The most common reasons for castration are a male dog’s excessive sexual interest, a female dog living in the same household, recurring prostate problems or illnesses where testosterone is a contributing factor (such as perineal hernia, perianal adenoma) and testicular tumours. In urban areas where there are many dogs, females in heat in the neighbourhood may also disturb a male dog’s life too much, which is when castration can reduce the dog’s and his owner’s stress.
Castration involves making one incision in front of the scrotum and removing both testicles through it. The stitches will be hidden. The dog will have to wear a cone for about a week to prevent licking. He will be given pain medication for a few days.
several rabbits in the household. This will prevent unnecessary fights.

Soft tissue surgery
In addition to neutralisation and castration, the most common operations we perform are various soft tissue surgeries. These include, for example, tumour removal, eyelid surgery, hernia repair, internal organ surgery and operations in the mouth and throat area.